GNEISS
Gneiss is a common high-grade, foliated metamorphic rock characterized by alternating bands of light- and dark-colored minerals. It forms by metamorphism of schists or felsic-to-intermediate intrusive igneous rocks (e.g., granite).
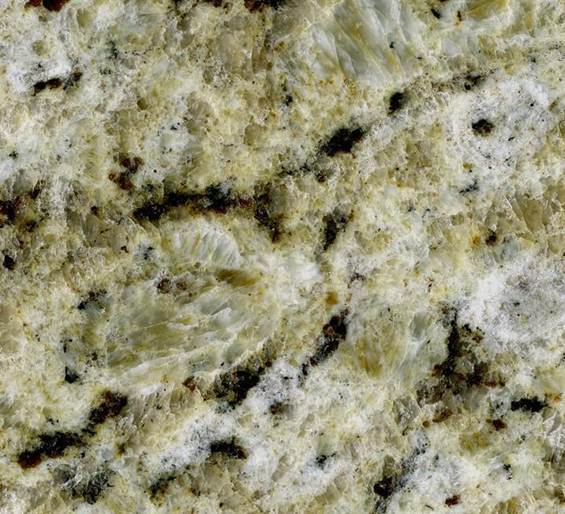
Venetian Gold Granite - a late Neoproterozoic to Cambrian-aged garnetiferous gneiss from Brazil. It's quarried at Nova Venecia, in Espirito Santo State, coastal southeastern Brazil. Metamorphism occurred at ~650-500 million years ago. It contains quartz, feldspar, mafic minerals, and very dark red garnets.
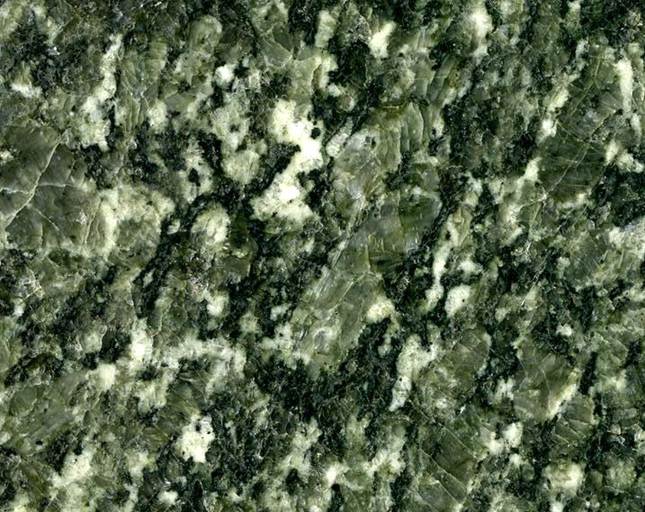
Verde Lavras Granite - a Paleoproterozoic (1.9 billion years) orthogneiss (metamonzogranite) from Lavras in Minas Gerais State, southeastern Brazil. The gneissic foliation is on a coarse scale, but is still recognizable (see elongated, large, greenish-gray feldspars & the elongated, irregularly wavy, black mafic areas). This rock has plagioclase feldspar, quartz, perthitic microcline feldspar, hornblende amphibole, and biotite mica.
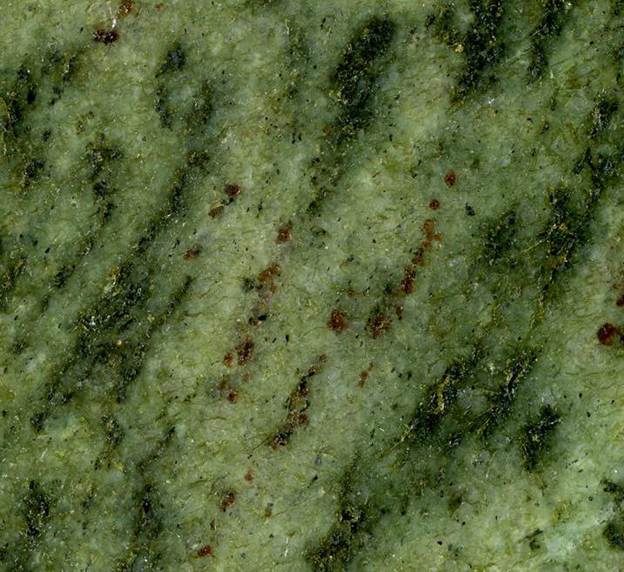
River Green Granite - a colorful garnetiferous gneiss with greenish quartz, spots of reddish garnets, and blackish-colored streaks of ferromagnesian minerals. Undetermined provenance & age.